“Computer is an electronic machine that can store, recall and process data. It can perform tasks or complex calculation according to a set of instructions or programs”.
Characteristics of Computer:
- Speed
- Storage
- Accuracy
- Diligence
- Versatility
- Flexibility
- Cost effectiveness
- Speed:
The computer works very fast. The speed of Computer is measured in terms of MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) or BIPS (Billion Instructions Per Second).
For Example A money counting machine counts money faster than man. - Storage:
The computer can store a large volume of data and information. The storage capacity of the computer is measured in terms of Bytes. A group of 8 Bits is called a Byte. - Accuracy
The computer-generated results are exact and without any mistakes with a high rate of consistency. - Diligence
Unlike human beings, a computer does not suffer from limitations like tiredness and lack of concentration. It can work for hours without making any errors. - Versatility
Computers are capable of performing any task. Multi-processing features of a computer make it quite versatile. The computer can be adapted to any field easily. It is used for scientific calculations, business processing, playing games, teaching, training, etc. - Flexibility
Flexibility would involve the number of things you can do with a computer. While some are best used for simple business tasks, and filing of tasks, others are good for multimedia, gaming, and so on. - Cost-effectiveness
Computers reduce the amount of paperwork and human effort, thereby reducing costs.
Data Processing
The computer system converts raw data into meaningful information. This process of converting raw data into meaningful information is called data processing.
Data: Refers to raw facts, figures, observations, or symbols that represent some aspect of the real world.
Example: Temperature readings, Numerical data, name, marks, etc.
Information: A processed and organized data with definite meaning is called information.
Examples: Weather forecast, financial data, medical diagnosis, etc.
Functional Parts of a Computer System
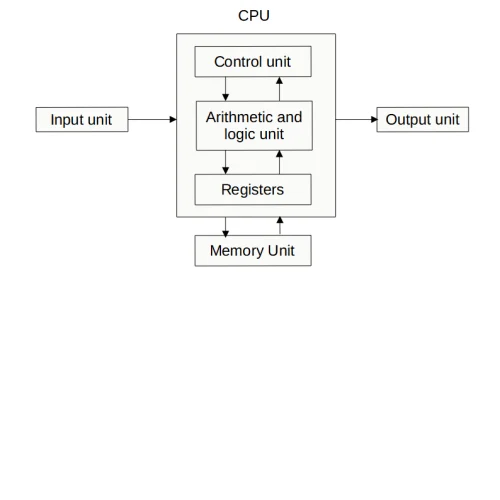
A computer system has the following parts.
Input unit: – A device used to input or feed the data into a computer system.
Examples: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, etc.
Central Processing Unit (CPU): – It is a main part of the computer system like a heart in the human body. The function of the CPU is to interpret the instructions in the program and execute them one by one.
CPU consists of following major units:
Memory Unit: The memory unit is also known as the primary storage or main memory (RAM). It stores data, program instructions, internal results, and final output temporarily before it is sent to an appropriate output device.
Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU): ALU is the unit where all Arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc.) and logical functions such as AND, OR NOT are performed.
Control unit: It coordinates all the input and output devices of a system. The control unit controls all the hardware operations i.e., those of input units, output units, memory unit, and the processor.
Storage Unit
Results obtained after processing will be in the primary memory, these data or information can be stored in the storage device/secondary memory units.
Output Unit
An output device is any hardware component that conveys information to one or more people.in user understandable form. Commonly used output devices are printer, monitor and speakers.